8th Grade Global Studies Syllabus
-
Phone Number: 651-293-8830
Course Description:
Students will actively engage in the work of a geographer by asking geographic questions and then acquiring, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting geographic information in order to answer geographic questions.
This course will use a regional approach to explore the 6 essential elements of Geography: Places and Regions, Physical Systems, Human Systems, Environments and Society, The Spatial World and Uses of Geography in Today’s Society. The content will incorporate a variety of scales – from local to global. Classroom materials will include adopted instructional materials and supplementary printed and electronic resources.
Expectations for students
- Participate in class discussions
- Participate and contribute to group work
- Complete homework and class assignments
Daily required materials
- a pen or pencil (sharpened before class)
- Social Studies materials
- your 3 ring binder including your planner
Guiding Questions of Geography:
- How do geographers organize information about the Earth?
- Where are things located?
- Why are they located there?
- How does the environment influence human activities?
- How do humans interact with and impact their environment?
- What are the physical and human characteristics of places?
- How does the movement of people affect place and culture?
- How are places interconnected and how are those connections changing?
Standards and Benchmarks:
Essential Skills
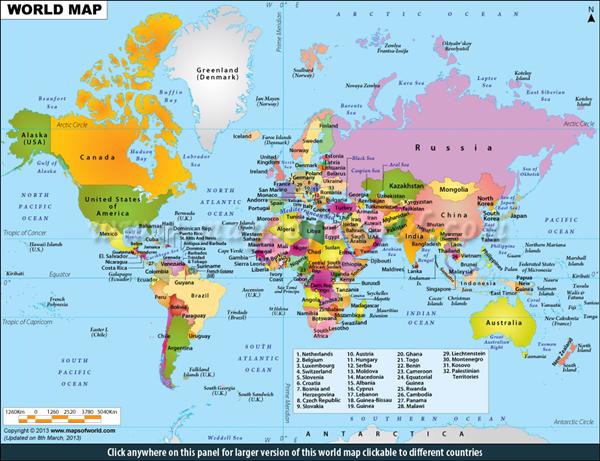
The student will use maps, globes, geographic information systems and other sources of information to analyze the natures of places at a variety of scales
Maps and Globe
The student will use maps and globes to demonstrate specific and increasingly complex geographic knowledge
The student will make and use maps to acquire, process, and report on the spatial organization of people and places on Earth.
Physical Features and Processes
The student will identify physical characteristics of places and use this knowledge to define regions, their relationships among regions, and their patterns of change.
Interconnection
The student will give examples that demonstrate how people are connectedto each other and the environment.
The student will describe how humans influence the environment and in turn are influenced by it.
The student will demonstrate how various regional frameworks are used to analyze the variation in culture and human occupation of the Earth’s surface.
Scope and Sequence
This course will use a regional approach and study the following thematic topics within each regional unit: physical and human systems, land use and resources, population and migration, industry and economic development.
Geographic Skills
Canada and US
Latin America
Africa South of the Sahara
Southwest Asia and North Africa
East Asia and Southeast Asia
Model United Nations
South Asia and Central Asia
Australia/Oceana
Content-based Instructional Practices (Habits of Thinking)
To think like a geographer students need these habits of thinking:
- Recognize spatial patterns.
- Use maps and other geographical tools (globes, atlases, tables, charts, graphs, documents) to acquire, analyze, organize and report information.
- Use mental maps to organize and analyze information about people, places, and environments.
- Apply geography to interpret the past, the present, and plan for the future.
- Analyze and interpret information obtained from maps, aerial photographs, satellite produced images, and geographic information systems
- Prepare various forms of maps, graphs, diagrams, table, or charts to organize and display geographic information