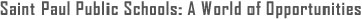Social Responsibility
-
As our motto says, "together we teach and guide learners to develop academic achievement and social responsibility."
Social Responsibility is the way we interact with each other as humans, and the earth, both inside and outside of the school building. We understand that children learn so much more than reading, writing, and math at school; they are also learning how to become kind humans and good citizens.
How do we focus on Social Responsibility? As a community, we focus on Social Responsibility through the use of Restorative Practices, Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports (PBIS), the Zones of Regulation, and Culturally Responsive Teaching.
PBIS
-
PBIS (Positive Behavior Intervention & Supports) is an evidence-based framework for supporting students' behavioral, academic, social, emotional, and mental health. It is a way to create positive, predictable, equitable and safe learning environments where everyone thrives.
PBIS implementation involves explicit teaching, practicing and reinforcement of schoolwide expectations in all settings. When students are taught to effectively use social skills with others, learning environments and relationships are described as more positive, safer, more trusting and respectful.
Restorative Practices

-
What is Restorative Practices?
Restorative Practices is a way of being in community with each other that fosters connection and a sense of belonging. It is based on principles and processes that emphasize the importance of positive, healthy relationships. At Cherokee Heights, our goal is for children, families, and educators to be happy to come to school every day and feel that they are connected to each other through healthy relationships. We build these relationships through the use of the Circle process, and when relationships have been harmed, Restorative Practices offers a pathway to repair the relationship. Mistakes are an opportunity for growth and learning, and Restorative Practices promotes problem-solving, inclusiveness, and relationship building rather than exclusionary punishment which does not offer a pathway for learning from mistakes. Children and adults in communities implementing Restorative Practices show improved empathy, kindness, collaboration, communication, and problem solving skills.
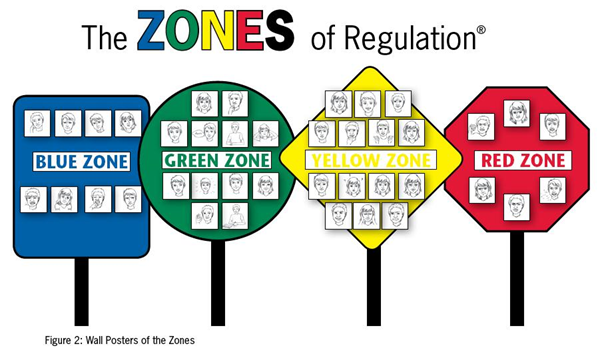
Zones of Regulation
-
Zones of Regulation is a system for children to learn to identify and name their feelings and develop tools to respond to "big" emotions. Children are better able to stay in the learning portions of their brain, rather than the reacting portions of their brain, when they can identify when they begin to feel frustrated, sad, hurt, angry, or any of the other emotions that might impact their ability to remain calm. Children are taught language about emotions and a variety of calming tools each month that help them stay in or get back to the "green zone" - the learning centers of the brain.
Culturally Responsive Teaching
-
Culturally Responsive Teaching and the Brain, by Zaretta Hammond, is a guide to help educators understand the many ways culture impacts learning. In her book, Hammond speaks directly to collectivism versus individualism and the way that positive relationships enhance the brain's ability to learn. Hammond notes that humans are "hardwired" for connection, which guides our work as educators at Cherokee Heights. Children and adults in our community are loved and valued for who they are authentically.
Social Responsibility Book of the Month
-
All Cherokee Heights classrooms read the book of the month, and participate in activities which support the following themes:
Self Identification
Growth Mindset
Kindness
Empathy
Self Control/Self Regulation
Integrity
Problem Solving
Justice
Cooperation